Eczema
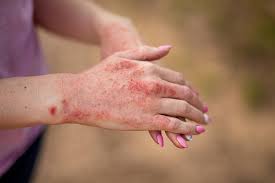
Eczema is a non-contagious skin condition that results in dry and itchy skin patches. In the event one gets in contact with irritant or an allergen it is likely this might trigger the symptoms of eczema. Eczema impacts the skin’s barrier function. This function is primarily responsible for helping your skin retain moisture and protecting the body from external elements, that may affect the skin.
- Atopic dermatitis:
It is a skin condition that results in inflammation, redness, and severe itching. It usually starts in childhood, however can affect all people across ages. - Contact dermatitis:
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition that cause inflammation by exposure of skin, to any chemical or physical agent. Symptoms of Contact dermatitis include, itchy or dry skin, red rash, bumps, blisters, and swelling - Dyshidrotic eczema:
Dyshidrotic eczema, also known as dyshidrosis, is a chronic skin condition, mostly common in people between the ages of 20 and 40, or with a family history of eczema of contact dermatitis that gives rise to small, itchy blisters and dry skin on the hands, feet, and sides of fingers. This is generally triggered by stress, and is common in people who work with products containing metals. - Neurodermatitis:
Neurodermatitis is a skin condition that is typically observed on the neck, wrists, forearms, legs or groin area. It forms as a small patch coupled with itching, scratching aggravates the itching leading the skin to be thick and leathery. - Nummular eczema:
Nummular eczema, also referred to as nummular dermatitis or discoid eczema, is a chronic skin condition that, leads to coin-shaped patches on the skin with a itching sensation. - Seborrheic dermatitis:
Seborrheic dermatitis is a commonly observed but non-contagious skin ailment that results in flaky, oily patches, and inflammation of the skin.
